ADFS identity provider initiated SSO and relaystate
I was recently tasked to setup a single sign on case between two web applications.
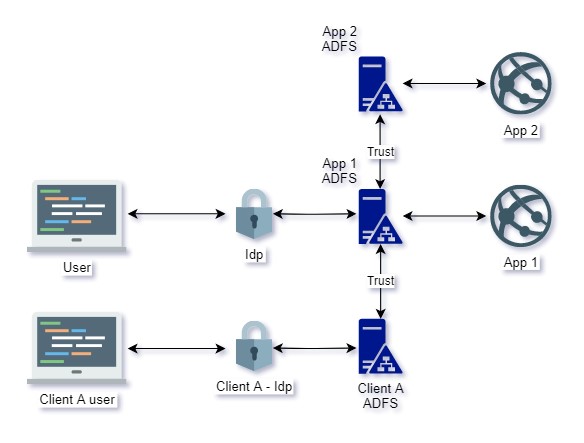
Application one (App 1) is a multi tenant SaaS offering using an identity provider, Idp, coupled with Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services, ADFS, for users to authenticate (App1 ADFS). Some of the users of this application use their corporate Idps to login, federating with application 1 (Client A ADFS).
 |
Federation Setup |
Application two (App 2) is SaaS, multi tenant, and accepts user authentication from another ADFS using SAML protocol (App2 ADFS).
Setting up the single sign on was relatively straightforward. I will skip the details here. Once it was in place users using application one idp was able to login to App1 and navigate to App2 seemlsly.
The more tricky part was to allow users of App1 who are using their corporate Idps to access App2. To Achieve this I decided to use Idp initiated SSO with relaystate to bypass any screens in between.
Microsoft.IdentityServer.Web.CookieManagers.InvalidContextException: MSIS7001: The passive protocol context was not found or not valid. If the context was stored in cookies, the cookies that were presented by the client were not valid. Ensure that the client browser is configured to accept cookies from this website and retry this request.
import urllib.parseimport sysif (len(sys.argv) != 5):print("Usage: python relayState.py idp_init_url fed1_rpid fed2_rpid app_rpid")exit()finalurl=sys.argv[1] + "?RelayState=" + urllib.parse.quote_plus("RPID=" + urllib.parse.quote_plus(sys.argv[2]) + "&RelayState=" + urllib.parse.quote_plus("RPID=" + urllib.parse.quote_plus(sys.argv[3]) + "&RelayState=") + urllib.parse.quote_plus("RPID=" + urllib.parse.quote_plus(sys.argv[4])))print(finalurl)
idp_init_url = Client A ADFS Idp initiated urlfed1_rpid = App1 ADFS identifierfed2_rpid = App2 ADFS identifierapp_rpid = App2 relying party identifier
Client A ADFS Idp initiated url: https://{clientA-ADFS-FQDN}/adfs/ls/idpinitiatedsignon.aspxApp1 ADFS identifier: http://{App1-ADFS-FQDN}/adfs/services/trustApp2 ADFS identifier: http://{App2-ADFS-FQDN}/adfs/services/trustApp2 relying party identifier: urn://application2/id
https://{clientA-ADFS-FQDN}/adfs/ls/idpinitiatedsignon.aspx?RelayState=RPID%3Dhttp%253A%252F%252F%257BApp1-ADFS-FQDN%257D%252Fadfs%252Fservices%252Ftrust%26RelayState%3DRPID%253Dhttp%25253A%25252F%25252F%25257BApp2-ADFS-FQDN%25257D%25252Fadfs%25252Fservices%25252Ftrust%2526RelayState%253DRPID%253Durn%25253A%25252F%25252Fapplication2%25252Fid
HTH
Comments
Post a Comment